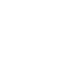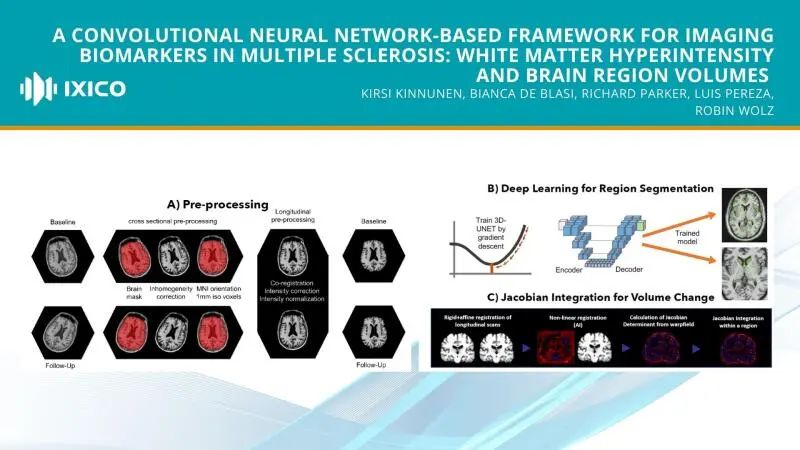
Summary:
We developed and validated scalable and robust methods for automated volumetric analysis of brain white matter hyperintensities (T2 lesions) and regions of interest in multiple sclerosis.
Method:
We trained Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to segment white matter hyperintensities (WMH) from 3D FLAIR scans and various brain regions from 3D T1W scans, including the thalamus and whole brain. We additionally measured whole-brain volume changes using Jacobian integration. We validated these methods on publicly available and internal datasets, using a consensus WMH segmentation as the ground truth for WMH and semi-automated segmentations as ground truths for brain regions. We assessed accuracy/robustness and test-retest performance.
Conclusion:
Our study demonstrated the accuracy of our WMH workflow; it outperformed other automated methods in terms of overlap and volume correlation with the ground truth. Furthermore, our brain region workflow provided high-quality and reliable results for the thalamus and whole-brain regions. The IXIQ.Ai framework offers a scalable and robust solution for the automated volumetric analysis of brain white matter hyperintensities and regions of interest in multiple sclerosis studies.
This was presented at ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS 2023 (MSMilan2023)