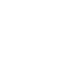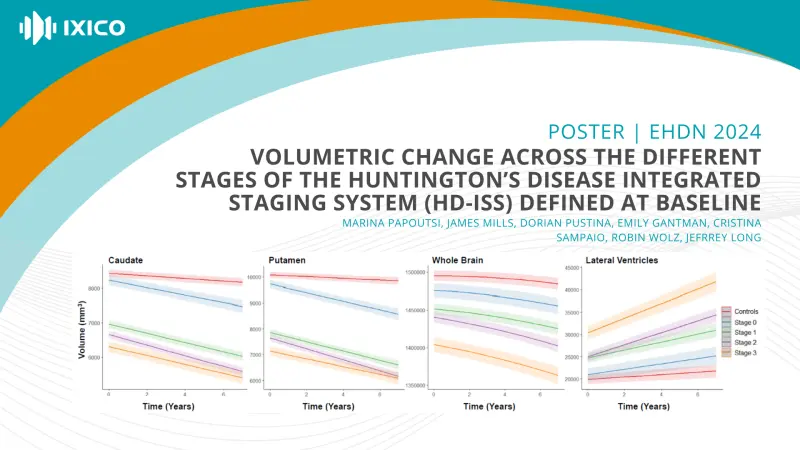
The HD Integrated Staging System enables classification of people with HD into four disease stages based on quantitative landmark assessments. Here we characterized volume change over time in the caudate nucleus, putamen, lateral ventricles, and
whole-brain across participants starting in each of the different HD-ISS Stages at baseline and compared to healthy controls.
We used a subset of data from TRACK-HD/ON and PREDICT-HD studies, which have been processed as part of the HD Imaging Harmonization (HD-IH) consortium. Volumetric analyses were performed using deep-learning and the generalized Boundary Shift
Integra methods.
Method
We analysed data from 482 controls and 1,219 participants with HD across the four HD-ISS stages. Demographic details at baseline entry into the study are provided in the table below. Visits up to 6.5 years were included in the analyses. To enable differentiation between HD-ISS Stages 0 and 1 within the HD-IH consortium data, new cut-off values were calculated based on the control study participants for the HD-ISS Stage 1 landmarks, i.e. the putamen and caudate volume, adjusted by the affine scaling factor (ASF; Buckner et al. 2004), using the IXIQ.Ai methods.
Results
For all regions, there was a significant main effect of group, time, and group by time interaction (all p<0.001 Bonferroni corrected for four ROIs).The results from the post-hoc comparisons of the group by time interaction within the HD-ISS groups. Comparisons against the control group were all significant (all p < 0.01 corrected). P-values were Tukey-adjusted for a family of 5 estimates and then Bonferroni
corrected for four ROIs.
Presented at EHDN 2024